The research area Industry and Production of the Lamarr Institute investigates the transformative role of Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) in optimizing processes in production engineering. In addition to ensuring high-quality production results, the research focuses on minimizing resource requirements, including time and material costs. Traditional approaches are often based on technological experiments or simulation-based optimization. However, the integration of ML provides a paradigm shift and enables, e.g., the identification of patterns and relationships in production data that was previously not possible.
In this blog post, you will learn how ML is shaping production engineering through innovative approaches and gain insights into a current research project that serves as a case study for advances in this area.
Improving production processes through Machine Learning
ML is revolutionizing the way complex production processes are being analyzed and optimized. By learning from large data sets, ML algorithms can generalize predictions across different scenarios and configurations and discover knowledge that is difficult to obtain with conventional methods. This capability is particularly beneficial in production engineering, where hybrid learning approaches can significantly reduce the experimental effort required to comprehend and improve production processes by combining data-based ML models with physics and domain-specific knowledge.
Within the research area Industry and Production at the Lamarr Institute, a key focus is on combining measurement data, simulation data and ML methods to develop hybrid models. These approaches support data science analysis in production contexts by augmenting datasets with synthetic data generated by advanced techniques such as simulations or generative modeling to reduce the manual effort of data mining and annotation for supervised learning tasks (Want to learn more about what types of machine learning exist? This way: Types of Machine Learning).
This systematic modeling allows data-based insights to be acquired that contribute to the optimization of industrial processes and enable resource-efficient production. The Lamarr Institute researches these methods in order to develop innovative AI technologies that improve data-driven decision-making processes in production. This bridges the gap between AI research and real industrial applications – a key contribution to designing sustainable and more precise production processes.
Another important aspect of this transformation is the integration of expert knowledge. The combination of data-driven modeling techniques with expert knowledge not only has the potential to increase the accuracy of model predictions, it also enables results to be interpreted, which leads to increased acceptance and more trust among practitioners. Interdisciplinary collaboration plays a crucial role in this. By bringing experts from different fields together, such as data science and manufacturing technology, complex challenges can be considered from multiple perspectives. This synergy not only improves the reliability of ML models, but also fosters innovation by bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application.
ClusterSim: Machine Learning and Expert Knowledge in Production Engineering
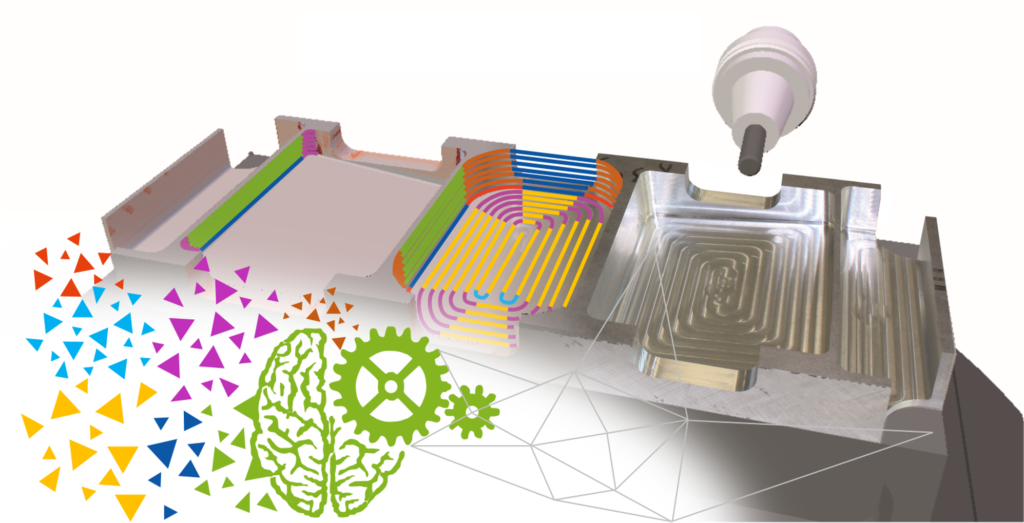
An exemplary cooperation project in this area is “ClusterSim”, in which the Virtual Machining working group (computer science) and the Institute of Machining Technology (mechanical engineering) at TU Dortmund University are involved. The project demonstrates how ML can be used purposefully in production engineering. The aim is to improve the analysis and prediction of characteristics of machining processes – such as tool vibrations, which can affect the quality of workpiece surfaces.
In contrast to conventional “black box” approaches, ClusterSim focuses on interpretability and generalization by combining ML with different data sources and technological expertise. The project focuses on the analysis of high-resolution time series data from experimental studies and geometric-physical process simulations. Unsupervised learning methods, such as Gaussian Mixture Models, can be used to identify recurring patterns in these data sets and group them into classes (see Fig. 1).

For each identified class, ML regression models are trained to predict process characteristics for different operating points. By dividing the data into these elementary process segments and the expert models trained on this basis for each of these segments, an increased prediction accuracy for very complex processes and interactions between influencing variables and resulting process characteristics, which cannot be represented in a single model, is made possible on the one hand. On the other hand, the ability of the model to be applied to different processes and configurations is improved, since it can provide reliable predictions for essentially any process that has similar patterns in its basic operations.
From Research to Practice: the Role of Innovation Networks
The integration of ML into production engineering is being advanced through collaboration with industry. One example of this is the innovation network Virtualization and AI in Machining Technology (INTSPA). Funded by the German Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Climate Action (BMWK) as part of the Central Innovation Programme for small and medium-sized enterprises (ZIM), this network brings together researchers and industry experts to study advanced ML and AI applications in metal-cutting manufacturing. By creating a structured platform for specialists, INTSPA enables the analysis and combination of complex topics such as machining processes, machine tools, cutting tools and quality assurance.
This collaboration enables the development of intelligent systems and applications for the entire value chain, which can improve the competitiveness of the industry. Companies benefit from customized solutions that optimize production processes, reduce costs and improve product quality. By combining academic research with real industrial challenges, the ZIM network is an example of how technological progress and economic growth in production engineering can be driven forward together.
Potential of Machine Learning for Transforming Production Engineering
The integration of ML into production engineering is initiating a new phase of economical and sustainable manufacturing. Through the automation of knowledge acquisition and the hybrid combination of models, data sources and expert knowledge, this field of research offers innovative and resource-efficient solutions for industrial applications. Interdisciplinary collaboration and the continuous advancement of ML technologies and their application in production engineering are laying the foundations for realizing the vision of automated, optimized, intelligent manufacturing systems that are both economical and sustainable.
Despite the significant progress in the application of ML in production engineering, several open research questions remain that will determine the direction of future work. A key challenge is the seamless integration of expert knowledge into data-driven ML approaches. While combining expert knowledge with ML models has proven effective in individual research investigations to improve accuracy and efficiency, there remains a need for standardized frameworks that enable such interdisciplinary collaboration on a large scale. In addition, concept drift, where process conditions and data distributions change over time, poses a challenge to ensuring robust prediction accuracy in dynamic production environments. Finally, promoting transparent and sustainable research data management practices is crucial to ensure the availability and reproducibility of data across the research community to enable long-term progress in the field.
